The Fertility Rainbow: Antioxidants for Women’s Hormonal Balance and Reproductive Health
The Fertility Rainbow: Antioxidants for Women’s Hormonal Balance and Reproductive Health
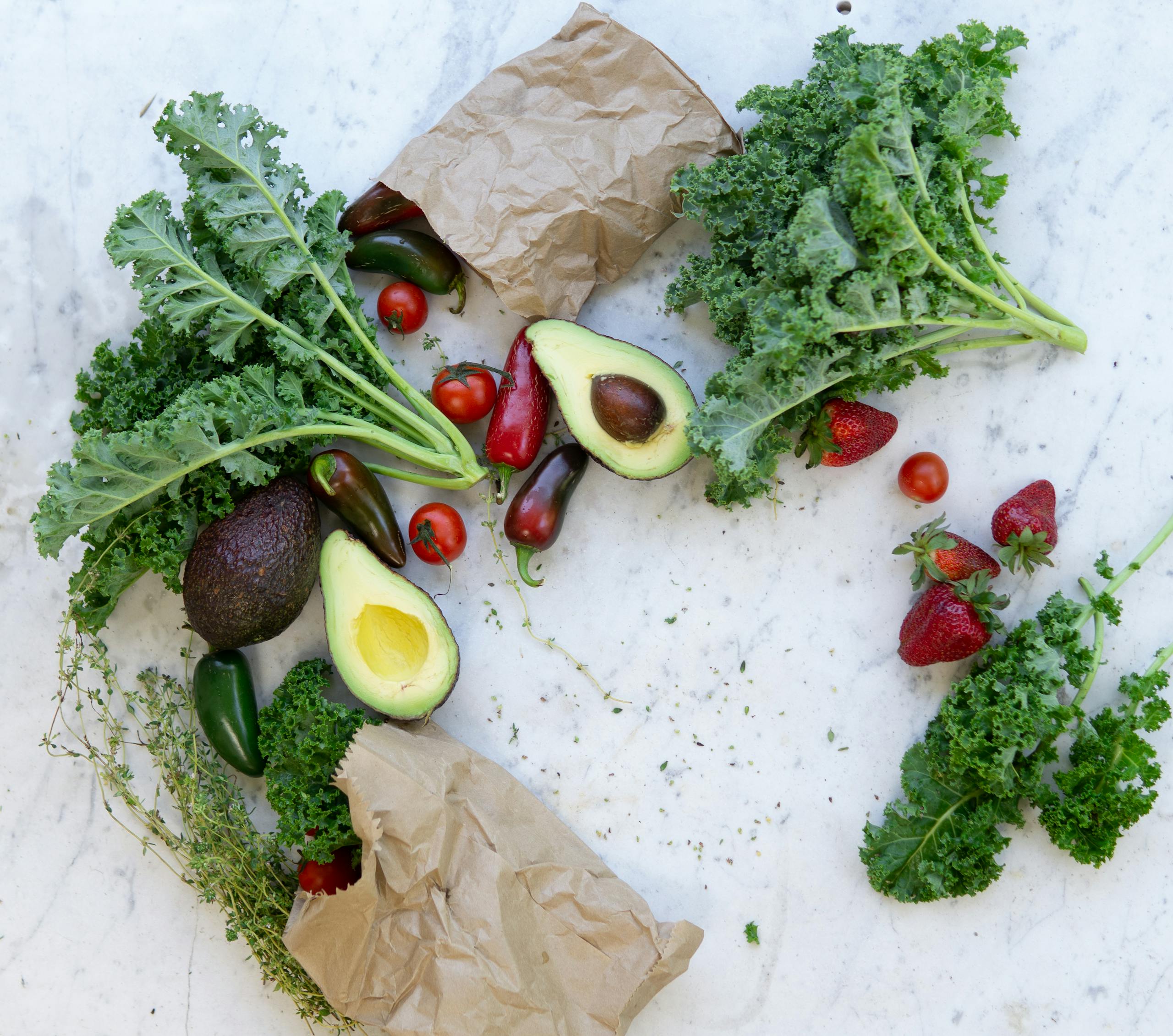
The journey toward optimal reproductive health is intricately linked to what we put on our plates. Just as with general well-being, the vibrant colors of fruits and vegetables hold a key to women’s hormonal balance, cycle regulation, and fertility success. The powerful compounds behind these colors are antioxidants—essential nutrients that combat the silent enemies of reproductive health: oxidative stress and chronic inflammation.
Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, can damage egg quality (oocytes), impair the function of the ovaries and uterus, and disrupt the delicate hormonal symphony that governs the menstrual cycle. By incorporating specific, color-coded antioxidants, women can build a protective shield around their reproductive system, supporting everything from egg maturation to a healthy uterine lining.
Red: Enhancing Circulation and Uterine Health
The brilliant reds of produce are a beacon for cardiovascular health, which is directly tied to reproductive success. Excellent blood flow is crucial for delivering hormones and nutrients to the ovaries and creating a thick, receptive uterine lining.
- Key Antioxidants: Lycopene and Anthocyanins.
- Source: Tomatoes (especially cooked), watermelon, strawberries, raspberries, pomegranates, and cherries.
- The Fertility Benefit:
- Lycopene: Found in abundance in tomatoes, lycopene’s potent antioxidant action helps improve blood flow and can protect the DNA within reproductive cells from damage. It is particularly known for reducing inflammation associated with conditions like endometriosis and uterine fibroids, which thrive in inflammatory environments.
- Anthocyanins: These compounds, plentiful in berries and pomegranates, are excellent at reducing systemic inflammation. By supporting vascular health, they ensure optimal blood supply to the pelvis, which is critical for egg development and implantation.
Orange & Yellow: Protecting Egg Quality and Boosting Progesterone
The golden hues of orange and yellow foods signal high levels of compounds vital for progesterone production and protection against cellular aging—both critical aspects of fertility.
- Key Antioxidants: Beta-Carotene and Vitamin C.
- Source: Carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkin, mangoes, cantaloupe, and oranges.
- The Fertility Benefit:
- Beta-Carotene: This powerful precursor to Vitamin A is essential for ovarian function and hormone synthesis. Studies suggest that diets rich in carotenoids may improve ovulation and increase serum progesterone levels, the hormone necessary for maintaining the second half of the cycle (luteal phase) and supporting early pregnancy.
- Vitamin C: Abundant in citrus and mangoes, Vitamin C is a potent water-soluble antioxidant. It plays a crucial role in the production of progesterone and helps protect the corpus luteum (the structure that produces progesterone after ovulation) from oxidative stress, thereby stabilizing the menstrual cycle. It is also vital for collagen formation, which is important for the ovarian and uterine tissues.
Green: Folate, Detoxification, and Estrogen Balance
Dark leafy greens are the undisputed champions of fertility nutrition, providing the foundation for DNA health and effective hormone metabolism.
- Key Antioxidants: Folate (B9), Lutein, Zeaxanthin, and Sulforaphane (in cruciferous greens).
- Source: Spinach, kale, broccoli, asparagus, and Brussels sprouts.
- The Fertility Benefit:
- Folate: Perhaps the most famous fertility nutrient, Folate is essential for DNA synthesis and repair in both the mother’s cells and the developing fetus, significantly reducing the risk of neural tube defects. It helps ensure optimal oocyte maturation and fertilization.
- Sulforaphane: Found in cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower), this compound supports the liver’s Phase II detoxification pathway. This is essential for effectively metabolizing excess or ‘spent’ estrogen out of the body, helping to mitigate conditions like estrogen dominance, which can worsen PMS, fibroids, and endometriosis.
- Lutein & Zeaxanthin: While known for eye health, their strong antioxidant power protects all rapidly dividing cells, including those in the reproductive system, from free radical damage.
Blue & Purple: Anti-Aging and Hormonal Stress Relief
The deep colors of blue and purple foods are loaded with compounds that protect the reproductive organs from the effects of time and environmental stressors.
- Key Antioxidants: Anthocyanins and Resveratrol.
- Source: Blueberries, blackberries, purple grapes, purple cabbage, and eggplant (with skin).
- The Fertility Benefit:
- Anthocyanins: These are crucial for their anti-aging effects on the ovaries. Ovarian reserve and egg quality naturally decline with age, a process driven by cumulative oxidative damage. Regular intake of blueberries and similar foods can help slow this process by neutralizing the free radicals responsible for cellular wear and tear.
- Resveratrol: Found in the skin of purple grapes, this polyphenol has been studied for its ability to improve ovarian response and may help modulate hormones by acting as a phytoestrogen (a plant-derived compound that weakly binds to estrogen receptors), supporting balance when native estrogen is low or erratic.
White & Tan: Insulin Sensitivity and Hormonal Regulation
While not as bright, the white and tan category offers critical compounds that address the often-overlooked factor in women’s hormonal health: blood sugar regulation and insulin sensitivity.
- Key Antioxidants: Allicin, Quercetin, and Chromium (in mushrooms).
- Source: Garlic, onions, mushrooms, and cauliflower.
- The Fertility Benefit:
- Quercetin: Found in onions, this flavonoid improves insulin sensitivity. Maintaining healthy insulin levels is paramount for hormonal balance, especially for women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), where insulin resistance is a major driver of elevated androgens and irregular cycles.
- Allicin: The key compound in garlic, allicin supports cardiovascular health and blood flow, ensuring that hormone-regulating messages and nutrients are delivered efficiently throughout the body. Its anti-inflammatory action also reduces the overall “hormonal noise” caused by chronic inflammation.
- Mushrooms: Certain compounds in mushrooms are known to support the immune system and also offer trace minerals like selenium, which is necessary for thyroid health, a gland crucial for fertility and metabolic regulation.
The Prescription: Eat a Colorful Plate, Not a Pill
A powerful, non-pharmacological strategy for boosting women’s hormonal and reproductive health is embracing the diversity of antioxidants found in the produce aisle. By ensuring that your daily diet includes components from the red, orange/yellow, green, blue/purple, and white/tan categories, you are providing your body with the synergistic protective compounds needed to:
- Protect and repair the delicate DNA of egg cells.
- Detoxify and metabolize hormones for proper estrogen and progesterone balance.
- Improve blood flow to the uterus and ovaries.
- Reduce inflammation that can impair cycle regularity and implantation.
Incorporating this “Fertility Rainbow” into every meal is a proactive and sustainable step toward achieving optimal hormonal balance and supporting the dream of a healthy pregnancy.
This information is educational and not medical advice. Consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis or treatment.